3D Printed Heart “Patch”: A Revolution in Regenerative Medicine
3D Printed Heart “Patch”: A Revolution in Regenerative Medicine
Recent advances in 3D printing are opening up new perspectives in the treatment of heart diseases, including myocardial infarctions. One of the most promising projects is the so-called “3D Printed Band-Aid” for the heart, which can significantly improve the ability to regeneration of cardiac tissue.
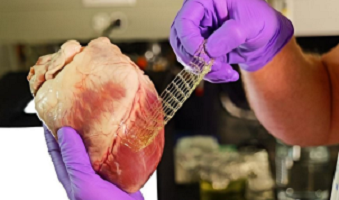 Cardiopatch Project: New Technologies for Treating Myocardial Infarctions
Cardiopatch Project: New Technologies for Treating Myocardial Infarctions
The Cardiopatch project, implemented by organizations from Spain, France and Portugal, focuses on the use of 3D printing technology in regenerative medicine. The main goal is to create a stem cell patch that could repairdamaged heart tissue without the need for invasive surgery. The patch is printed using advanced bioprinting techniques and is designed to promote transport, culture and implantation into the site of heart injury.
The technology uses stem cells placed on a collagen membrane enriched with cardioprotective agents. Preliminary studies have shown that this approach has therapeutic potential, which has been confirmed in initial in vivo trials in animal models. By using a specially designed 3D bioreactor, it is possible to efficiently grow and transport these slices.
 Advantages and Potential Applications of 3D Patches
Advantages and Potential Applications of 3D Patches
The main advantage of this solution is the possibility of minimally invasive implantation of the patch, which significantly reduces the risk of complications and speeds up the healing process. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of heart disease, offering an alternative to current methods such as pharmacotherapy or heart transplants, which are fraught with many limitations.
The Cardiopatch project is supported by European Union funding programs, allowing for further research development and potential implementation of the technology on a wider scale. European research resources and structures play a key role in promoting collaboration between medicine and 3D printing technology, contributing to advances in the field of regenerative medicine.
One of the key aspects of the technology is the use of 3D printed structures that can be precisely tailored to a patient’s individual needs. This process allows for the creation of more precise and effective therapies, which is particularly important in the treatment of complex heart conditions.
The Future of Regenerative Medicine with 3D Printing
In conclusion, the development of 3D printing technology in medicine offers new opportunities in the treatment of heart disease. The Cardiopatch project is an example of how advanced technologies can be used to create innovative solutions that can significantly improve the quality of life for patients with heart disease. While there are still many challenges ahead, the results so far are very promising and point to potentially groundbreaking developments in cardiac therapy.
Advanced technologies such as 3D printing have the potential to revolutionize many aspects of medicine, including cardiac tissue regeneration. With further research and financial support, it is possible that in the future the treatment of heart attacks will be more effective and accessible to a wider range of patients.
Challenges and Prospects
Despite the promising results, researchers still face numerous challenges. Further clinical trials are needed to confirm the efficacy and safety of this technology in humans. Additionally, there is a need to develop more advanced methods to monitor and control the regeneration process to ensure the best therapeutic results.
In addition, the implementation of new technologies in clinical practice requires the cooperation of many sectors, including medicine, technology and government. It is also crucial to increasing public awareness of the potential of regenerative medicine and support for research and innovation in this area.
In light of the rising incidence of heart disease worldwide, the development of technologies such as Cardiopatch could prove crucial in the fight against these conditions. Further investment in research and development could yield breakthroughs that improve the quality of patients’ lives and reduce the burden on healthcare systems.
Summary
3D printing technology in regenerative medicine offers unprecedented opportunities to treatments for heart disease. The Cardiopatch project is a step toward more effective and less invasive therapies that can significantly improve patient outcomes and quality of life patients. Continued research and technology development in this area has the potential to revolutionize cardiovascular medicine in the near future.
Maja Bracichowicz


